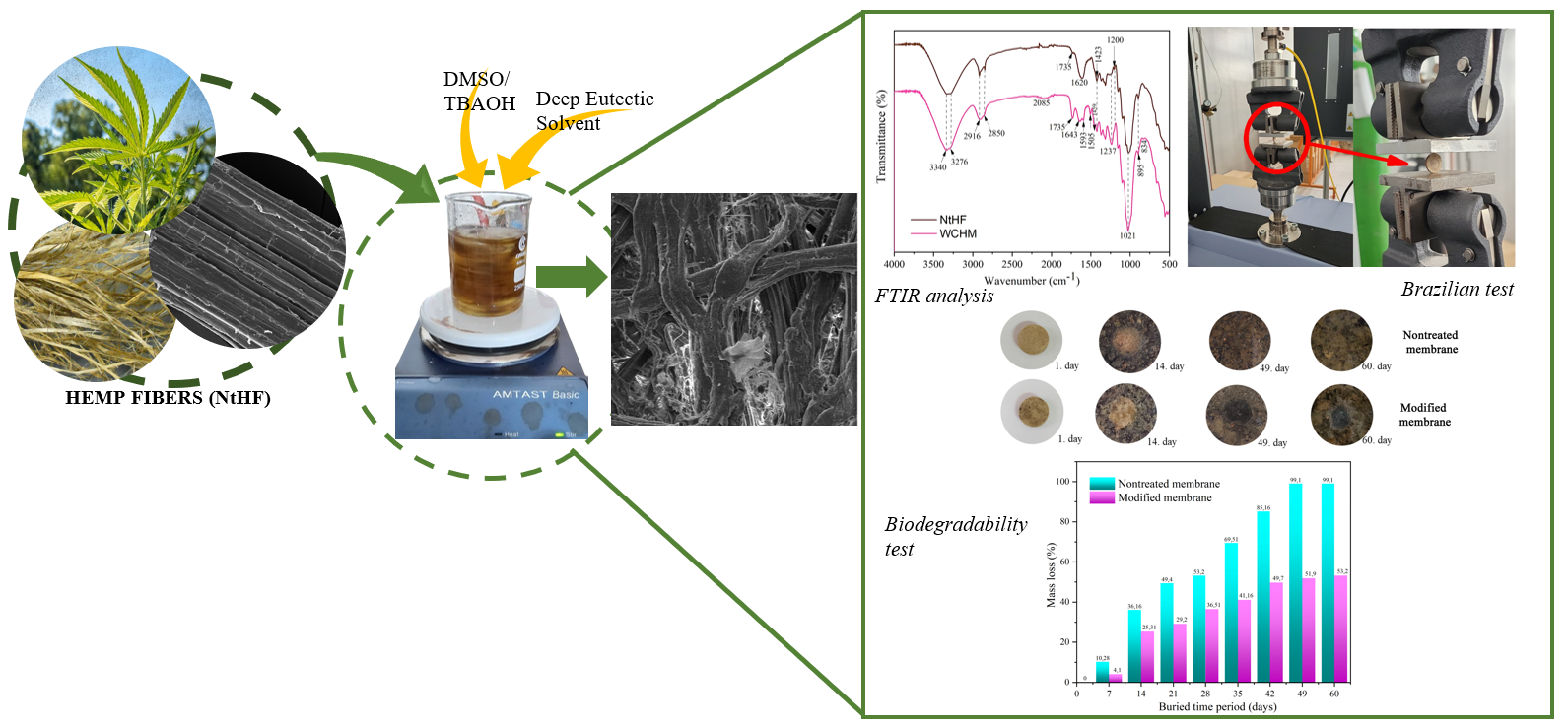
Enhanced Mechanical Strength and Controlled Biodegradability of Bio-Membranes Synthesized from Waste Hemp Fibers
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.30544/MMD71Abstract
In this work, agricultural hemp waste was converted into cationically modified membranes through a two-step procedure. First, the post-harvest hemp fibers underwent delignification, after which they were quaternized using a Deep Eutectic Solvent (DES) composed of chlorocholine chloride and urea. The cationized fibers were then pressed and cross-linked with citric acid (CA), a natural cross-linker, to obtain membrane sheets. The untreated fibers (NtHF) and the resulting membranes were characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). Mechanical performance was evaluated by measuring the breaking force and determining the tensile strength using the Brazilian test. Biodegradation was monitored for 90 days in a controlled soil-burial environment at 24 °C, comparing membranes made from untreated versus cationized hemp fibers. The modified material exhibited a notable increase in tensile strength (2.41 MPa), attributed to the combined effects of enhanced intermolecular interactions within the cationic hemp matrix and the stronger cross-linking provided by citric acid. Signs of biodegradation appeared after just 14 days, with approximately 25% mass loss. In contrast, the untreated fibers degraded slightly faster, underscoring the stabilizing effect of citric acid.
Keywords:
hemp fibers, biodegradability, mechanical properties, Brazilian test, Deep eutectic solventReferences
Arora, S., Gupta, N. and Singh, V., Choline Based Basic Ionic Liquid (BIL)/Acidic DES Mediated Cellulose Rich Fractionation of Agricultural Waste Biomass and Valorization to 5-HMF, Waste and Biomass Valorization, vol. 11, no. 7, pp. 3345-54, July 4, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-019-00603-2
Brunšek, R., Kopitar, D., Schwarz, I. and Marasović, P., Biodegradation Properties of Cellulose Fibers and PLA Biopolymer, Polymers, vol. 15, no. 17, p. 3532, August 24, 2023. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15173532
Fairhurst, C., On the Validity of the 'Brazilian' Test for Brittle Materials, International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences & Geomechanics Abstracts, vol. 1, no. 4, pp. 535-46, October 1964. https://doi.org/10.1016/0148-9062(64)90060-9
Kalisz, G., Gieroba, B., Chrobak, O., Suchora, M., Starosta, A. L. and Sroka-Bartnicka, A., Vibrational Spectroscopic Analyses and Imaging of the Early Middle Ages Hemp Bast Fibres Recovered from Lake Sediments, Molecules, vol. 26, no. 5, p. 1314, March 1, 2021. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26051314
Knežević, N., Milanović, J., Veličković, Z., Milošević, M., Vuksanović, M. M., Onjia, A. and Marinković, A., A Closed Cycle of Sustainable Development: Effective Removal and Desorption of Lead and Dyes Using an Oxidized Cellulose Membrane, Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, vol. 126, pp. 520-36, October 2023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2023.06.041
Knežević, N., Vuksanović, M. M., Banjanac, K., Pantić, K., Veličković, Z., Cvijetić, I., Marinković, A. and Milošević, M., Cationic Waste Hemp Fibers-Based Membrane: Case Study of Anionic Pollutants Removal through Environmentally Friendly Processes, Journal of Environmental Management, vol. 371, p. 123174, December 2024a. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2024.123174
Knežević, N., Vuksanović, M. M., Banjanac, K., Pantić, K., Veličković, Z., Cvijetić, I., Marinković, A. and Milošević, M., Cationic Waste Hemp Fibers-Based Membrane: Case Study of Anionic Pollutants Removal through Environmentally Friendly Processes, Journal of Environmental Management, vol. 371, p. 123174, December 2024b. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2024.123174
Matykiewicz, D., Barczewski, M., Mysiukiewicz, O. and Skórczewska, K., Comparison of Various Chemical Treatments Efficiency in Relation to the Properties of Flax, Hemp Fibers and Cotton Trichomes, Journal of Natural Fibers, vol. 18, no. 5, pp. 735-51, May 4, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1080/15440478.2019.1645792
Navidtehrani, Y., Betegón, C., Zimmerman, R. W. and Martínez-Pañeda, E., Griffith-Based Analysis of Crack Initiation Location in a Brazilian Test, International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, vol. 159, p. 105227, November 2022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2022.105227
Pejić, B., Vukčević, M. and Kostić, M., Hemp Fibers in Serbia: Cultivation, Processing and Applications, pp. 111-46, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-41384-2_4
Šebestík, J., Marques, S. M., Falé, P. L., Santos, S., Arduíno, D. M., Cardoso, S. M., Oliveira, C. R., Serralheiro, M. L. M. and Santos, M. A., Bifunctional Phenolic-Choline Conjugates as Anti-Oxidants and Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors, Journal of Enzyme Inhibition and Medicinal Chemistry, vol. 26, no. 4, pp. 485-97, August 1, 2011. https://doi.org/10.3109/14756366.2010.529806
Sirviö, J. A. and Lakovaara, M., A Fast Dissolution Pretreatment to Produce Strong Regenerated Cellulose Nanofibers via Mechanical Disintegration, Biomacromolecules, vol. 22, no. 8, pp. 3366-76, August 9, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biomac.1c00466
Viscusi, G., Barra, G. and Gorrasi, G., Modification of Hemp Fibers through Alkaline Attack Assisted by Mechanical Milling: Effect of Processing Time on the Morphology of the System, Cellulose, vol. 27, no. 15, pp. 8653-65, October 25, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03406-0
Wen, Q., Chen, J.-X., Tang, Y.-L., Wang, J. and Yang, Z., Assessing the Toxicity and Biodegradability of Deep Eutectic Solvents, Chemosphere, vol. 132, pp. 63-69, August 2015. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.02.061
Yang, Z., Asoh, T.-A. and Uyama, H., Cationic Functionalization of Cellulose Monoliths Using a Urea-Choline Based Deep Eutectic Solvent and Their Applications, Polymer Degradation and Stability, vol. 160, pp. 126-35, February 2019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2018.12.015
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Nataša Knežević, Marija Vuksanović, Aleksandar Marinković

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.